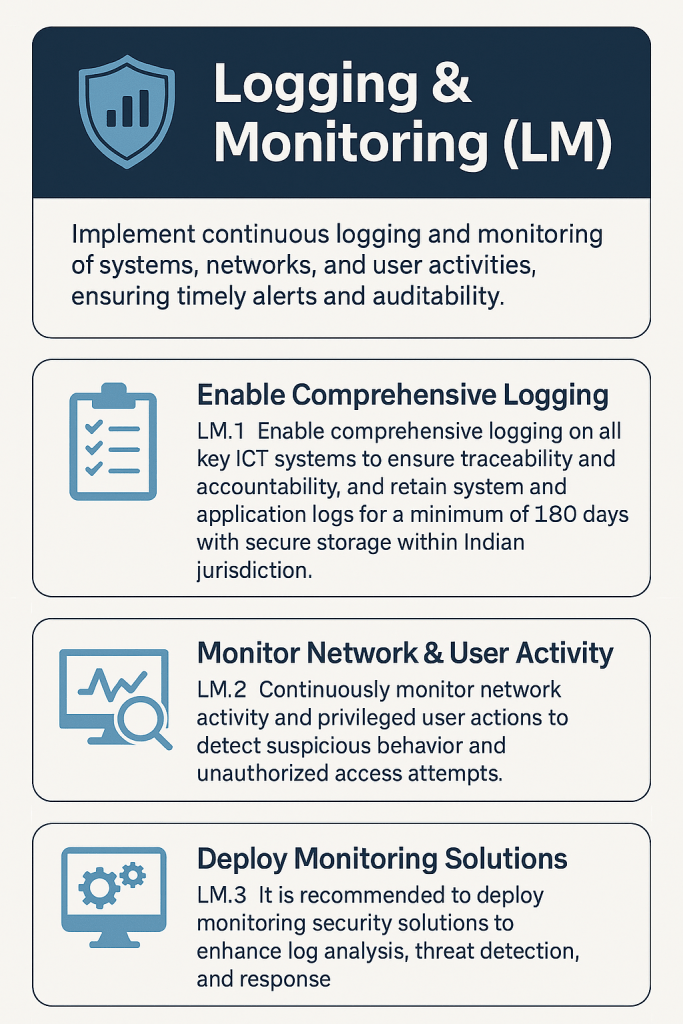
In cybersecurity, not every threat comes with flashing lights and alarms. Some creep in quietly through unauthorized access, privilege misuse, or suspicious network activity. That’s why Logging and Monitoring (LM) is essential. It’s the silent guardian that watches, records, and alerts when something goes wrong.
This blog explores how Indian organizations, especially in the financial sector, can implement continuous logging and monitoring to ensure traceability, accountability, and compliance with national regulations.
What is Logging and Monitoring?
Logging is the process of recording events and activities across your IT systems like who logged in, what files were accessed, and which commands were executed.
Monitoring is the act of watching these logs in real-time or near-real-time to detect anomalies, threats, or policy violations.
Together, they form the backbone of cyber incident detection and response.
LM.1 Enable Comprehensive Logging Across All Key ICT Systems
Start by enabling logging on all critical systems:
- Servers and databases
- Firewalls and routers
- Applications and cloud platforms
- User access and authentication systems
Logs should capture:
- User activities (logins, file access, changes)
- System events (errors, updates, restarts)
- Network traffic (IP addresses, ports, protocols)
Example: A private bank in Mumbai configures its core banking system to log every admin login, transaction override, and failed access attempt.
Retention & Storage:
- Retain logs for at least 180 days.
- Store logs securely within Indian jurisdiction to comply with data localization norms.
Tip: Use encrypted storage and access controls to prevent tampering.
LM.2 Monitor Network Activity & Privileged User Actions
Monitoring should focus on:
- Privileged users (admins, developers, auditors)
- Network traffic (unusual data transfers, port scans)
- Access patterns (logins from unknown locations or odd hours)
Use tools like:
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)
- IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems)
- Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR)
Example: A fintech firm in Bengaluru uses a SIEM tool to detect when a developer accesses production data outside business hours.
LM.3 Deploy Security Monitoring Solutions
To make sense of massive log data, deploy smart tools that offer:
- Automated log analysis
- Real-time threat detection
- Alerting and incident response workflows
Popular solutions include:
- Splunk
- ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana)
- QRadar
- Azure Sentinel
Choose tools that integrate well with your existing infrastructure and support Indian compliance standards.
Compliance Snapshot
- RBI Cybersecurity Framework: Emphasizes logging and monitoring for banks and NBFCs.
- CERT-In Guidelines: Require timely detection and reporting of cyber incidents.
- IT Act, 2000 (Section 70B): Mandates secure logging and incident reporting.
Final Thoughts
Logging and Monitoring may not be flashy, but they’re critical for cybersecurity hygiene. By enabling comprehensive logging, monitoring privileged actions, and deploying smart analysis tools, organizations can detect threats early, respond faster, and stay compliant.
In a world where cyber threats evolve daily, LM is your first alert system quietly working behind the scenes to keep your digital assets safe.

Leave a comment